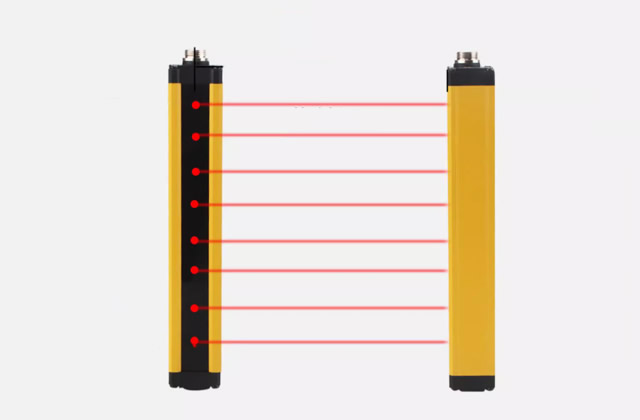
1. Working principle of infrared sensors
The physics behind infrared sensors is determined by three laws: ① Planck’s radiation law: temperature T is not equal to 0 K Every object emits radiation; ② Stephan Boltzmann’s law: The total energy emitted by a black body at all wavelengths is related to the absolute temperature; ③ Wein’s displacement law: The spectra emitted by objects at different temperatures reach peaks at different wavelengths; all temperatures are greater than absolute zero (0 Kelvin) objects have thermal energy and are therefore sources of infrared radiation.
Infrared sensor working principle process:
1. Target to be sided. The infrared system can be set according to the infrared radiation characteristics of the target to be approached.
2. Atmospheric attenuation. When the infrared radiation of the target to be measured passes through the earth’s atmosphere, the infrared radiation emitted by the infrared source will be attenuated due to the scattering and absorption of gas molecules, various gases, and various sol particles.
3. Optical receiver. It receives part of the target’s infrared radiation and transmits it to the infrared sensor. Equivalent to a radar antenna, commonly used as an objective lens.
4. Radiation modulator. Modulates the radiation from the target to be measured into alternating radiation, provides target orientation information, and can filter out large-area interference signals. Also known as modulators and choppers, it has a variety of structures.
5. Infrared detector. This is the core of the infrared system. It is a sensor that detects infrared radiation by using the physical effects caused by the interaction between infrared radiation and matter. In most cases, it uses the electrical effects caused by this interaction. Such detectors can be divided into two types: photon detectors and thermal sensitive detectors.
6. Detector cooler. Since some detectors must work at low temperatures, the corresponding system must have refrigeration equipment. After cooling, the equipment can shorten the response time and improve the detection sensitivity.
7. Signal processing system. Amplify and filter the detected signals, and extract information from these signals. This information is then converted into the required format and finally transmitted to the control device or display.
8. Display equipment. This is the terminal device for infrared devices. Commonly used displays include oscilloscopes, picture tubes, infrared photosensitive materials, indicating instruments and recorders, etc.
Following the above process, the infrared system can complete the measurement of the corresponding physical quantities.
2. What are the types of infrared sensors?
According to different emission methods, infrared sensors can be divided into activeThere are two types: passive and passive.
1. The transmitter of the active infrared sensor emits a modulated infrared beam, which is received by the infrared receiver, thereby forming a warning line composed of infrared beams. When it is blocked by leaves, rain, small animals, snow, dust, or fog, the alarm should not be alarmed. If it is blocked by people or objects of considerable size, the alarm will occur.
2. Passive infrared sensors work by detecting infrared rays emitted by the human body. The sensor collects infrared radiation from the outside and concentrates it on the infrared sensor. Infrared sensors usually use pyroelectric elements. When this element receives infrared radiation and changes in temperature, it will release charges and generate an alarm after detection and processing.
If the website content violates your rights, please contact us to delete it。