1. What are the technical parameters of the bridge crane?
The main technical parameters of the bridge crane include lifting capacity, span, lifting height, operating speed, lifting speed, and work type. And the energization duration rate of the motor, etc.
1. Lifting capacity
Lifting capacity, also known as rated lifting capacity, refers to the actual maximum lifting load allowed by the crane, measured in tons (t). unit.
The lifting capacity of bridge crane is 5, 10 (single hook), 15/3, 20/5, 30/5, 50/lO, 75/20, 100/20, 125/20, 150 /30, 200/30, 250/30t (double hook) and other types. The numerator in the number is the main hook lifting weight, and the denominator is the secondary hook lifting weight. For example, for a 15t/3t crane, the rated lifting capacity of the main hook is 15t and the rated lifting capacity of the auxiliary hook is 3t.
Overhead cranes can be divided into three levels according to their lifting capacity. Small cranes with 5 to 10 tons, medium-sized cranes with 10 to 50 tons, and heavy cranes with more than 50 tons.
2. Span
The span of an overhead crane refers to the distance between the center lines of the wheels at both ends of the crane’s main beam, that is, the distance between the center lines of the trolley track distance, in meters (m).
The spans of overhead cranes include 10.5, 13.5, 16.5, 19.5, 22.5, 25.5, 28.5, 31.5m, etc. Every 3m is a level.
3. Lifting height
The upper limit position and the lower limit position of the crane’s spreader or grabbing device (such as grab bucket, electromagnetic chuck) The distance between them is called the lifting height of the crane, measured in meters (m).
The commonly used lifting heights of cranes are 12, 16, 12/14, 12/18, 16/18, 19/21, 20/22, 21/23, 22/26, 24/26m, etc. Several kinds. The numerator is the lifting height of the main hook, and the denominator is the lifting height of the auxiliary hook.

4. Operating speed
The operating speed refers to the corresponding speed of the moving mechanism of the large and small vehicles when the driving motor runs at the rated speed, measured in meters/minute (m /min) as the unit. The running speed of small cars is generally 40~60m/min, and the running speed of large cars is generally 100~135m/min.
5. Increase speed
The speed at which the motor of the lifting mechanism raises the weight at the rated speed is the lifting speed. Generally, the lifting speed does not exceed 30m/min, which is determined according to the nature, weight and lifting requirements of the heavy object.
The lifting speed also includes the empty hook speed. The empty hook speed can shorten the non-production time, and the empty hook speed can be as high as twice the rated lifting speed.
There is a special case of lifting speed. The low speed when heavy objects are close to the ground is called low landing speed to ensure personal safety and cargo safety. Its speed is generally 4~6 m/min.
6. Work type
The work type of the crane is determined by its load rate and work busyness, and can be divided into light, medium, heavy and Four types of extra heavy grades.
(1) Light level. Slow running speed and infrequent use? There is little chance of being fully loaded, and the power-on continuity rate is 15%. For use in non-stressful and non-heavy workplaces. For example, it is used as a crane for installation and maintenance in hydropower stations and power plants.
(2) Intermediate level. It often works under different loads, with medium speed, not too heavy work, and power continuity rate of 25%, such as cranes used in general machining workshops and assembly workshops.
(3) Heavy level. The work is heavy, often working under heavy loads, and the power continuity rate is 40%, such as cranes used in metallurgical and foundry workshops.
(4) Extra heavy level. The rated load is often lifted, the work is particularly busy, and the power continuity rate is 60%, such as a bridge crane dedicated to metallurgy.
7. Power continuity rate
Each motor of the bridge crane works intermittently during a working cycle, and the heavy workload depends on the The power continuity rate is expressed as JC%. The power-on duration rate is the percentage of working time and working cycle, that is,
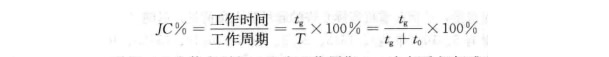
In the formula: 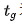 is the power-on time;
is the power-on time; 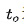 is the rest Time; T is the working cycle, and the standard working cycle of a crane is usually set to 10 minutes. The standard power-on duration rate is set to 1There are four types: 5%, 25%, 40% and 60%.
is the rest Time; T is the working cycle, and the standard working cycle of a crane is usually set to 10 minutes. The standard power-on duration rate is set to 1There are four types: 5%, 25%, 40% and 60%.
2. Complete specifications and models of bridge cranes
1. LDA model 1-20t Electric single-girder crane
2. LX model 0.5-5t electric single-girder suspension crane
3. LB model 1-10t explosion-proof electric single-girder crane
4 , LXB model 0.5-5t explosion-proof electric single-beam suspension crane
5. LH model 5-32/10t electric hoist bridge crane
6. QD model 5-50/10t crane Hook
7. QD model 75/20-100/20t hook overhead crane
8. QD model 100/32-250/50t hook overhead crane
9. QD model 75/20-125/50t casting crane
10. QC model 5-16t electromagnetic bridge crane
11. QC model 16-32- 32/5t electromagnetic bridge crane
12. QZ model 5-20t grappling bridge crane
13. QD model 5-50t slow-speed hook bridge crane
14. QD model 5-32t ground-operated hook bridge crane
15. QY model 5-50t insulated hook bridge crane
16. QD model 5 -50t variable frequency speed-adjustable bridge crane
17. QB model 5-50t explosion-proof hook bridge crane
18. LDZ model 3-5t electric beam grab crane
p>
19. SDQ model 1-10t manual single-girder crane
20. SDXQ model 0.5-3t manual single-girder suspension crane
21. SSQ model 5- 20t manual double girder crane
If the website content violates your rights, please contact us to delete it。








